Computer Architecture
Data Representation
Estimated Marks : 5
A lot of topic from this chapter you have already learned in Digital Logic and Microprocessor. If you dont know base conversion, binary codes types, you can check out 1st semester Digital Logic (Binary systems). Most importantly you must make strong foundation in signed number system as it will be used so much in this subject.
 Base conversion to Decimal
Base conversion to Decimal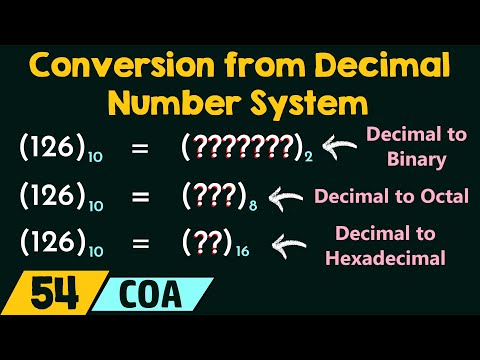 Base Conversion from Decimal
Base Conversion from Decimal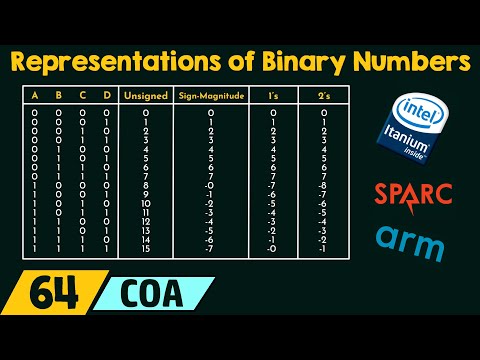 Binary Representation
Binary Representation Overflow Detection
Overflow Detection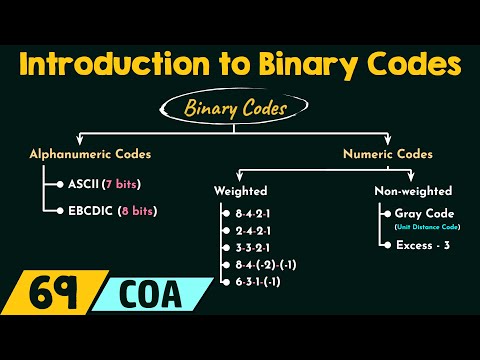 Binary Codes - Intro
Binary Codes - Intro Binary Code - Excess 3
Binary Code - Excess 3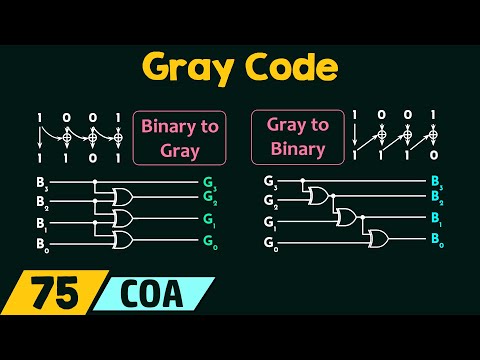 Binary Codes - Gray Code
Binary Codes - Gray Code Floating Points - 1
Floating Points - 1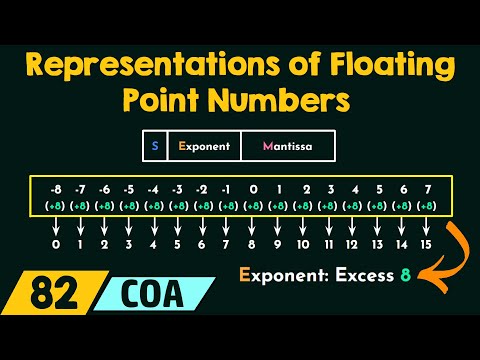 Floating Point - 2
Floating Point - 2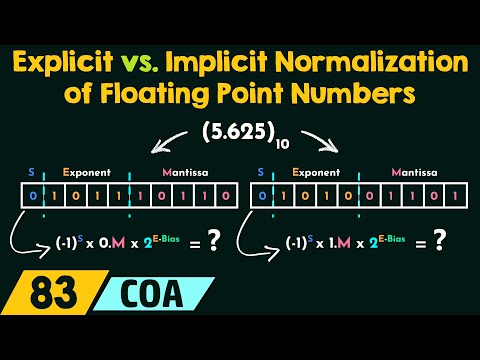 Floating Point - 3
Floating Point - 3 Parity - Error Detection
Parity - Error Detection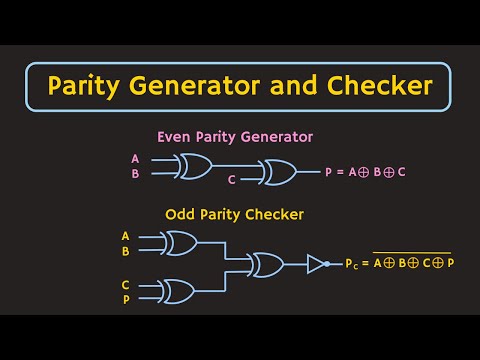 Parity Generator & Checker
Parity Generator & Checker- 1Base conversion to Decimal
- 2Base Conversion from Decimal
- 3Binary Representation
- 4Overflow Detection
- 5Binary Codes - Intro
- 6Binary Code - Excess 3
- 7Binary Codes - Gray Code
- 8Floating Points - 1
- 9Floating Point - 2
- 10Floating Point - 3
- 11Parity - Error Detection
- 12Parity Generator & Checker
Register Transfer and Microoperations
Estimated Marks : 5
This chapter teaches Register Transfer Language, Microoperations, Adder Circuit, Logic Circuits and Shift Circuits. In short you will learn to make a simple ALU.
 Register Transfer Language & Microoperations One Shot
Register Transfer Language & Microoperations One Shot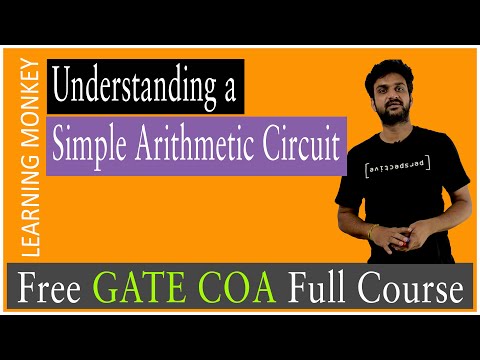 Arithmetic Circuit
Arithmetic Circuit- 1Register Transfer Language & Microoperations One Shot
- 2Arithmetic Circuit
Basic Computer Architecture
Estimated Marks : 10
This chapter is more wide (or difficult) than others. You will learn how control unit works, how instruction cycle works, how instruction is provided. There are many flowcharts and timing diagram here in this chapter.
 Common Bus System
Common Bus System  Computer Instruction Format
Computer Instruction Format  Timing and Control Unit
Timing and Control Unit Instruction Cycle
Instruction Cycle  Flowchart for Instruction Cycle
Flowchart for Instruction Cycle AND to AC and ADD to AC Memory Reference Instructions
AND to AC and ADD to AC Memory Reference Instructions LDA Load to AC and STA Store to AC Memory Reference Instructions
LDA Load to AC and STA Store to AC Memory Reference Instructions BUN Branch Unconditionally Memory Reference Instruction
BUN Branch Unconditionally Memory Reference Instruction BSA Branch and Save Return Address Memory Reference Instruction
BSA Branch and Save Return Address Memory Reference Instruction ISZ Increment and Skip if Zero Memory Reference Instruction
ISZ Increment and Skip if Zero Memory Reference Instruction Input-Output Configuration of Basic Computer
Input-Output Configuration of Basic Computer Input Output Instructions
Input Output Instructions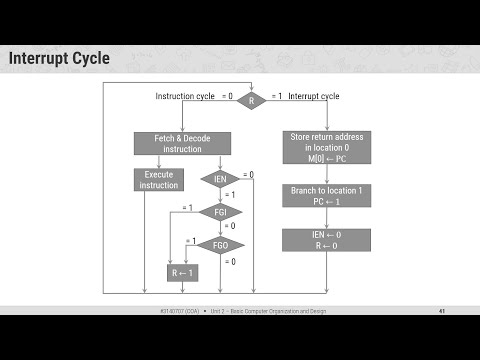 Interrupt Cycle
Interrupt Cycle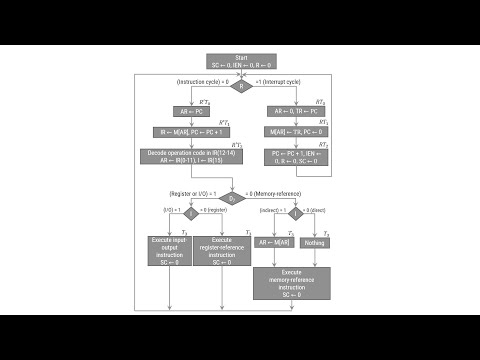 Complete Computer Description
Complete Computer Description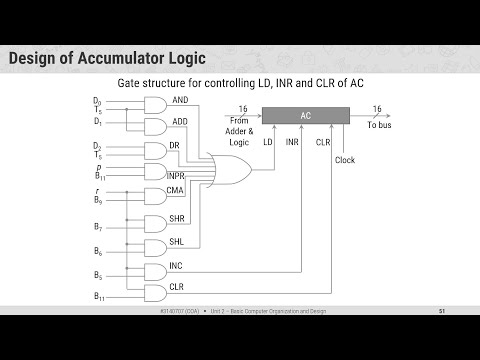 Design of Accumulator Logic
Design of Accumulator Logic- 1Common Bus System
- 2Computer Instruction Format
- 3Timing and Control Unit
- 4Instruction Cycle
- 5Flowchart for Instruction Cycle
- 6AND to AC and ADD to AC Memory Reference Instructions
- 7LDA Load to AC and STA Store to AC Memory Reference Instructions
- 8BUN Branch Unconditionally Memory Reference Instruction
- 9BSA Branch and Save Return Address Memory Reference Instruction
- 10ISZ Increment and Skip if Zero Memory Reference Instruction
- 11Input-Output Configuration of Basic Computer
- 12Input Output Instructions
- 13 Interrupt Cycle
- 14Complete Computer Description
- 15Design of Accumulator Logic
Microprogrammed Control
Estimated Marks : 5
This chapter focuses on the microprogramming aspect of control unit. U wil learn the basic structure of microprogrammed control unit, instruction format , adressing and some other components of control unit.
 Microprogrammed Control Unit
Microprogrammed Control Unit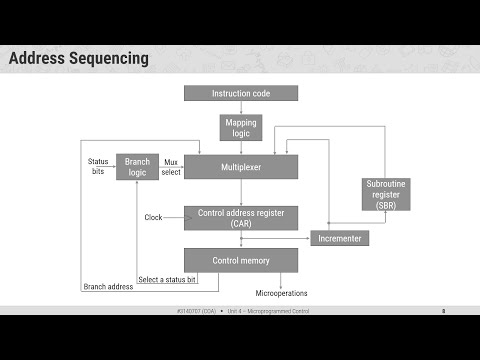 Address Sequencing
Address Sequencing Mapping of Instructions
Mapping of Instructions  Computer Configuration of Microprogrammed Control Unit
Computer Configuration of Microprogrammed Control Unit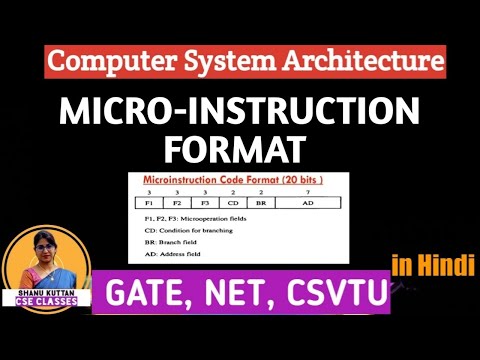 Microinstruction Format
Microinstruction Format Decoding of Microoperation Fields
Decoding of Microoperation Fields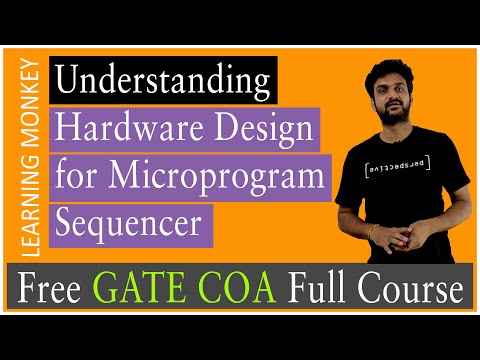 Hardware Design for Microprogram Sequencer
Hardware Design for Microprogram Sequencer- 1Microprogrammed Control Unit
- 2Address Sequencing
- 3Mapping of Instructions
- 4Computer Configuration of Microprogrammed Control Unit
- 5Microinstruction Format
- 6Decoding of Microoperation Fields
- 7Hardware Design for Microprogram Sequencer
CPU
Estimated Marks : 10
This is a comparatively easy chapter, here you wil learn about stack, instructions, addressing mode, interrupts and so on. Not entirely new things
 General Register Organization
General Register Organization Stack Organization, Register Stack & Memory Stack
Stack Organization, Register Stack & Memory Stack Instruction Formats
Instruction Formats Addressing Modes
Addressing Modes Data Transfer & Manipulation Instructions
Data Transfer & Manipulation Instructions Program Control, Status Bit Conditions & Conditional Branch Instructions
Program Control, Status Bit Conditions & Conditional Branch Instructions Program Interrupt, Types of interrupts
Program Interrupt, Types of interrupts RISC & CISC, Overlapped Register Window
RISC & CISC, Overlapped Register Window- 1General Register Organization
- 2Stack Organization, Register Stack & Memory Stack
- 3Instruction Formats
- 4Addressing Modes
- 5Data Transfer & Manipulation Instructions
- 6Program Control, Status Bit Conditions & Conditional Branch Instructions
- 7 Program Interrupt, Types of interrupts
- 8RISC & CISC, Overlapped Register Window
Pipelining
Estimated Marks : 10
One of the important chapters, pipelining hazards are one of the most asked questions and other topics are also important. Read well
 Flynn's Classification & Parallel Processing
Flynn's Classification & Parallel Processing Pipelining Introduction and structure
Pipelining Introduction and structure Pipelining Vs Non-Pipelining
Pipelining Vs Non-Pipelining Arithmetic Pipeline
Arithmetic Pipeline Instruction Pipeline
Instruction Pipeline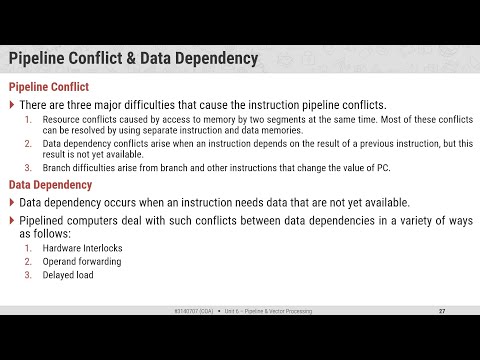 Pipeline Conflict (Hazards)
Pipeline Conflict (Hazards)  RISC Pipeline
RISC Pipeline Vector Processing
Vector Processing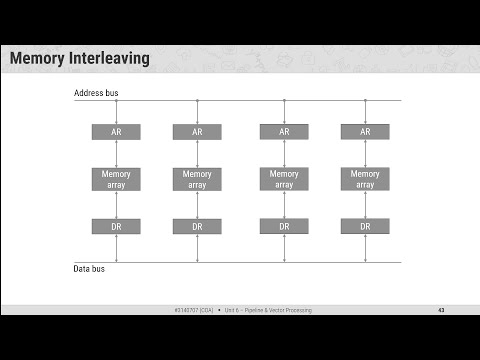 Memory Interleaving
Memory Interleaving  Array Processors & Attached Array Processor
Array Processors & Attached Array Processor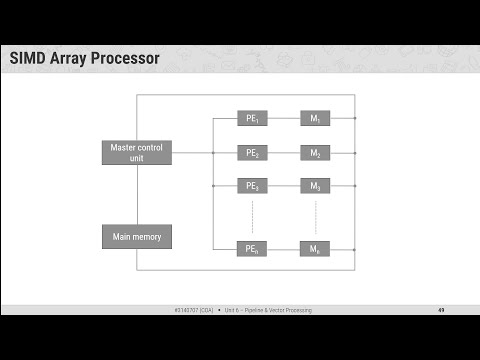 SIMD Array Processor
SIMD Array Processor - 1Flynn's Classification & Parallel Processing
- 2Pipelining Introduction and structure
- 3Pipelining Vs Non-Pipelining
- 4Arithmetic Pipeline
- 5Instruction Pipeline
- 6Pipeline Conflict (Hazards)
- 7RISC Pipeline
- 8 Vector Processing
- 9Memory Interleaving
- 10Array Processors & Attached Array Processor
- 11SIMD Array Processor
Computer Arithmetic
Estimated Marks : 10
One of the most important chapter. It is easy but you must take some time to practise. There are few topics: Addition, Multiplication and Division Algorithm. But before starting this chapter, you must understand signed number representation (watch chapter 1: Signed Number)
 Add & Subtract - Signed
Add & Subtract - Signed Multiplication - Signed Magnitude
Multiplication - Signed Magnitude Booths Algorithm
Booths Algorithm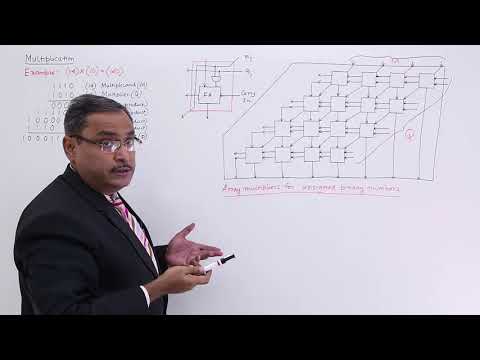 Array Multiplier
Array Multiplier Division Algorithm
Division Algorithm- 1Add & Subtract - Signed
- 2Multiplication - Signed Magnitude
- 3Booths Algorithm
- 4Array Multiplier
- 5Division Algorithm
Input & Output
Estimated Marks : 5
A simple chapter, where you will learn about how IO is interfaced and interrupt is handled in computer. These topics are super easy if you have studied interrupt in Microprocessor (even if you dont remember dont worry). Also you can watch at 1.5x or 2x speed, as there is no very difficult concept, just quickly skim through over this chapter.
 I/O Interface and Commands
I/O Interface and Commands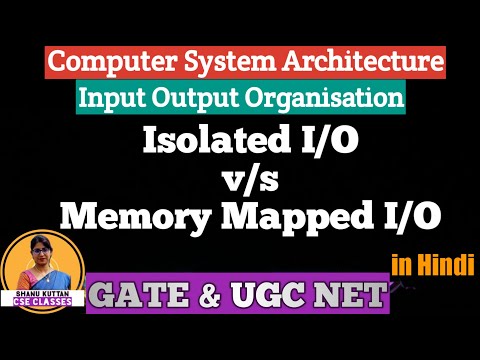 IO Mapping
IO Mapping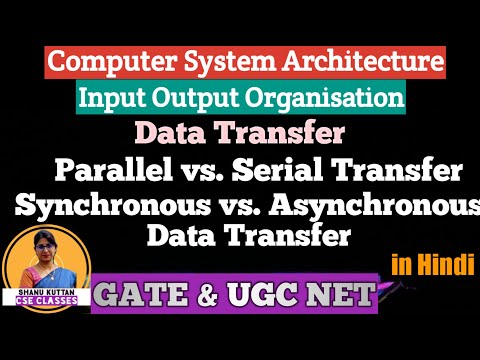 Data Transfer & Parallel vs Serial
Data Transfer & Parallel vs Serial Async Data Transfer - Part 1
Async Data Transfer - Part 1 Async. Data Transfer - Part 2
Async. Data Transfer - Part 2 Async Data Transfer - Part 3
Async Data Transfer - Part 3 Async Serial Transmission
Async Serial Transmission Modes of Transfer - Intro
Modes of Transfer - Intro Modes of Transfer - Programmed IO
Modes of Transfer - Programmed IO Modes of Transfer - Interrupt Initiated IO
Modes of Transfer - Interrupt Initiated IO Modes of Transfer - DMA
Modes of Transfer - DMA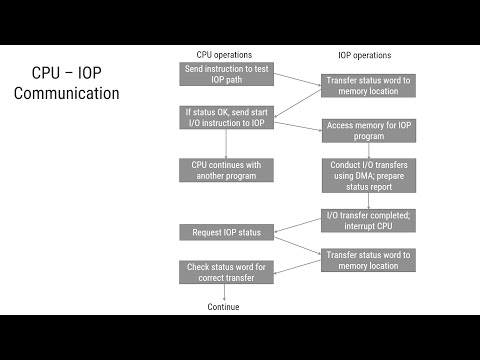 CPU IOP Communication
CPU IOP Communication Interrupt Concept
Interrupt Concept Priority Interrupt - Polling
Priority Interrupt - Polling Priority Interrupt - Daisy Chaining
Priority Interrupt - Daisy Chaining Priority Interrupt - Parallel Priority Interrupt
Priority Interrupt - Parallel Priority Interrupt- 1I/O Interface and Commands
- 2IO Mapping
- 3Data Transfer & Parallel vs Serial
- 4Async Data Transfer - Part 1
- 5Async. Data Transfer - Part 2
- 6Async Data Transfer - Part 3
- 7Async Serial Transmission
- 8Modes of Transfer - Intro
- 9Modes of Transfer - Programmed IO
- 10Modes of Transfer - Interrupt Initiated IO
- 11Modes of Transfer - DMA
- 12CPU IOP Communication
- 13Interrupt Concept
- 14Priority Interrupt - Polling
- 15Priority Interrupt - Daisy Chaining
- 16Priority Interrupt - Parallel Priority Interrupt
Memory Organization
Estimated Marks : 5
Small chapter on memory. SOON